为什么不推荐使用Executors提供的生成线程池的方法呢?
主要是因为这些线程池都存在内存溢出的可能。其实就是构建线程池的几个参数设置的不好,具体分析如下
Executors生成线程池的方法都是调用的ThreadPoolExecutor的构造方法,只不过提供了一些默认的参数,让我们使用起来更加方便。
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)参数的具体含义如下:
- corePoolSize 是核心线程数量。
- maximumPoolSize 是线程池容纳线程的最大数量。
- keepAliveTime 是空闲线程的存活时间
- TimeUnit 是KeepAliveTime的单位
- workQueue 是线程池用到的缓冲队列
- threadFactory 是创建线程的工厂
- handler 是线程池拒绝任务时的策略
线程池执行的逻辑和参数的关系可以用下面的图片来表示
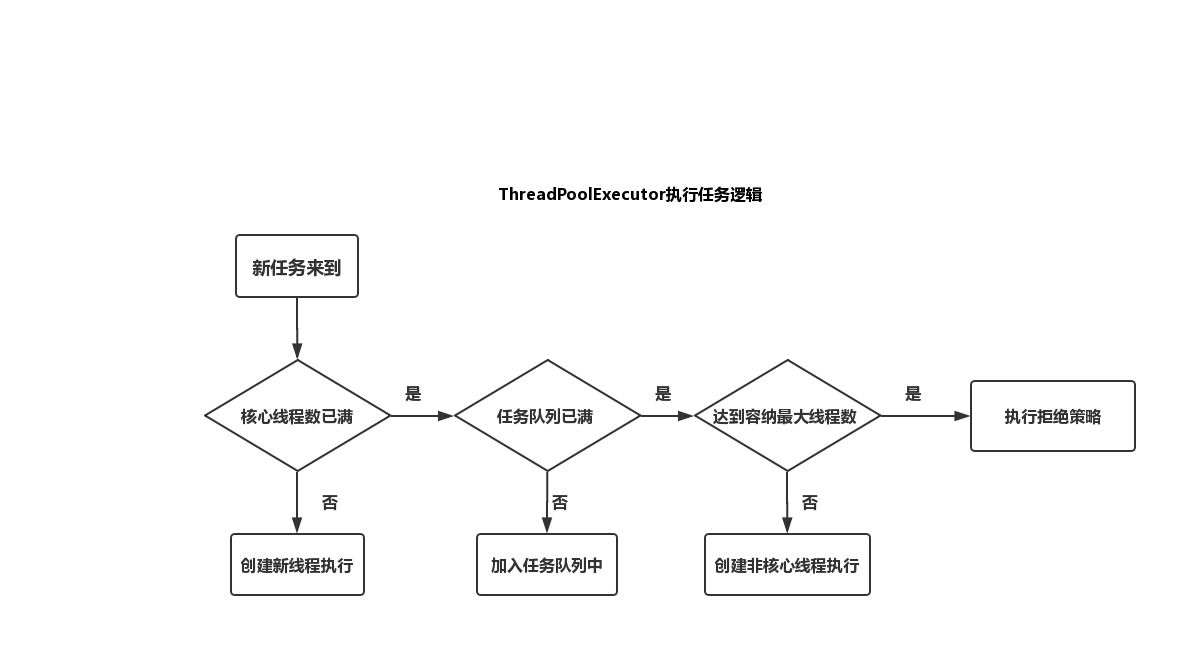
就是三个判断条件,核心线程数,任务队列是否满了,最大线程数量,如果三个条件同时达到就执行拒绝策略。
有了这个就能分析Executers的提供的创建线程池方法了
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}可以看到固定线程池,它使用了LinkedBolockingQueue作为任务队列,该队类的长度是Integer.Max,在内存低的时候会出现oom。
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}对于CacheeThreadPool而言,最大线程数量是Integer.MAX_VALUE,这个肯定是不行的,在内存低的时候,容易发生oom。
// newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()会执行到下面的方法
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}这个也不必多说,最大线程数设置为Integer.MAX_VALEU,这肯定是不可以的。
综上不推荐使用Executors生成线程池的主要原都是最大线程数量设置为Integer.MAX_VALUE,或者使用无界队列。其实根本原因是对线程池的最线程数量没有做一个限制。
来源地址:
https://blog.csdn.net/xiaoYuDAxiao/article/details/103133086
作者:Jeebiz 创建时间:2020-06-17 09:55
更新时间:2025-07-19 11:45
更新时间:2025-07-19 11:45
