Apereo CAS :自定义登录成功后的返回信息
Apereo CAS 与第三方单点认证成功后,默认返回的信息比较少或者可用的信息不多,使得第三方在编写接入的逻辑代码时,会比较不便。因此,我们需要改造 Apereo CAS 登录方法,追加 扩展信息
- 1、修改 Apereo CAS 的登录方法,追加 扩展信息
- 2、修改 Apereo CAS 的验票方法
/p3/validate,实时获取Redis缓存中的动态信息
修改 Apereo CAS 的 票据校验方法
1、引入 Maven 依赖
Apereo CAS 当前主要是采用 Overlay 的方式进行扩展。要想找到验证相关的对象,需要将相关的依赖项添加到项目的 Maven pom.xml 文件中:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apereo.cas</groupId>
<artifactId>cas-server-support-validation</artifactId>
<version>${cas.version}</version>
</dependency>然后找到 cas-server-support-validation,展开包结构,我们可以看到如下图所示效果:
2、分析源码
首先找到 CAS Client 的单点对接,进行登录验证的 API 入口:
| URI | 描述 |
|---|---|
| /validate | service ticket validation [CAS 1.0] |
| /serviceValidate | service ticket validation [CAS 2.0] |
| /proxyValidate | service/proxy ticket validation [CAS 2.0] |
| /proxy | proxy ticket service [CAS 2.0] |
| /p3/serviceValidate | service ticket validation [CAS 3.0] |
| /p3/proxyValidate | service/proxy ticket validation [CAS 3.0] |
- /p3/proxyValidate :
V3ProxyValidateController中的handle方法@GetMapping(path = CasProtocolConstants.ENDPOINT_PROXY_VALIDATE_V3) @Override protected ModelAndView handle(final HttpServletRequest request, final HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { return super.handleRequestInternal(request, response); } - /p3/serviceValidate :
V3ServiceValidateController中的handle方法@GetMapping(path = CasProtocolConstants.ENDPOINT_SERVICE_VALIDATE_V3) protected ModelAndView handle(final HttpServletRequest request, final HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { return super.handleRequestInternal(request, response); }
从两个方法的代码可见,除暴露的地址不同,代码逻辑都是一样的,最终都会进入父类 AbstractServiceValidateController 的 handleRequestInternal 方法;
该方法执行逻辑如下:
- 从请求中提取参数
- 检查参数,缺少参数时会跳到失败页面
- 准备票据验证的空方法,可用于扩展自定义前置逻辑
- 处理票据验证
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequestInternal(final HttpServletRequest request, final HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 提取请求参数
final WebApplicationService service = this.argumentExtractor.extractService(request);
final String serviceTicketId = service != null ? service.getArtifactId() : null;
// 参数检查,缺少参数时会跳到失败页面
if (service == null || !StringUtils.hasText(serviceTicketId)) {
LOGGER.debug("Could not identify service and/or service ticket for service: [{}]", service);
return generateErrorView(CasProtocolConstants.ERROR_CODE_INVALID_REQUEST, null, request, service);
}
try {
// 准备票据验证的空方法,可用于扩展自定义前置逻辑
prepareForTicketValidation(request, service, serviceTicketId);
// 处理票据验证
return handleTicketValidation(request, service, serviceTicketId);
} catch (final AbstractTicketValidationException e) {
final String code = e.getCode();
return generateErrorView(code, new Object[]{serviceTicketId, e.getService().getId(), service.getId()}, request, service);
} catch (final AbstractTicketException e) {
return generateErrorView(e.getCode(), new Object[]{serviceTicketId}, request, service);
} catch (final UnauthorizedProxyingException e) {
return generateErrorView(CasProtocolConstants.ERROR_CODE_UNAUTHORIZED_SERVICE_PROXY, new Object[]{service.getId()}, request, service);
} catch (final UnauthorizedServiceException | PrincipalException e) {
return generateErrorView(CasProtocolConstants.ERROR_CODE_UNAUTHORIZED_SERVICE, null, request, service);
}
}继续跟踪上面的方法中有返回结果的 generateErrorView 和 handleTicketValidation 方法,查看具体逻辑
generateErrorView 方法:
private ModelAndView generateErrorView(final String code, final Object[] args, final HttpServletRequest request, final WebApplicationService service) {
// 根据获取 ModelAndView 对象
final ModelAndView modelAndView = getModelAndView(request, false, service);
// 填充返回的内容属性
final String convertedDescription = this.applicationContext.getMessage(code, args, code, request.getLocale());
modelAndView.addObject(CasViewConstants.MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_NAME_ERROR_CODE, StringEscapeUtils.escapeHtml4(code));
modelAndView.addObject(CasViewConstants.MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_NAME_ERROR_DESCRIPTION, StringEscapeUtils.escapeHtml4(convertedDescription));
return modelAndView;
}handleTicketValidation 方法:
protected ModelAndView handleTicketValidation(final HttpServletRequest request, final WebApplicationService service, final String serviceTicketId) {
TicketGrantingTicket proxyGrantingTicketId = null;
// 从请求中获取服务凭据
final Credential serviceCredential = getServiceCredentialsFromRequest(service, request);
if (serviceCredential != null) {
try {
// 处理代理 GT 传递
proxyGrantingTicketId = handleProxyGrantingTicketDelivery(serviceTicketId, serviceCredential);
} catch (final AuthenticationException e) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to authenticate service credential [{}]", serviceCredential);
// 遇到异常,返回错误视图
return generateErrorView(CasProtocolConstants.ERROR_CODE_INVALID_PROXY_CALLBACK, new Object[]{serviceCredential.getId()}, request, service);
} catch (final InvalidTicketException e) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to create proxy granting ticket due to an invalid ticket for [{}]", serviceCredential, e);
// 遇到异常,返回错误视图
return generateErrorView(e.getCode(), new Object[]{serviceTicketId}, request, service);
} catch (final AbstractTicketException e) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to create proxy granting ticket for [{}]", serviceCredential, e);
// 遇到异常,返回错误视图
return generateErrorView(e.getCode(), new Object[]{serviceCredential.getId()}, request, service);
}
}
// 验证服务凭据,并返回 Assertion 对象
final Assertion assertion = validateServiceTicket(service, serviceTicketId);
// 验证服务票据 Assertion 信息
if (!validateAssertion(request, serviceTicketId, assertion, service)) {
// 验证不通过,返回错误视图
return generateErrorView(CasProtocolConstants.ERROR_CODE_INVALID_TICKET, new Object[]{serviceTicketId}, request, service);
}
// 验证认证上下文
final Pair<Boolean, Optional<MultifactorAuthenticationProvider>> ctxResult = validateAuthenticationContext(assertion, request);
if (!ctxResult.getKey()) {
// 验证不通过,返回错误视图
throw new UnsatisfiedAuthenticationContextTicketValidationException(assertion.getService());
}
String proxyIou = null;
if (serviceCredential != null && this.proxyHandler != null && this.proxyHandler.canHandle(serviceCredential)) {
// 获取 proxyIou
proxyIou = handleProxyIouDelivery(serviceCredential, proxyGrantingTicketId);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(proxyIou)) {
// 未获取到,返回错误视图
return generateErrorView(CasProtocolConstants.ERROR_CODE_INVALID_PROXY_CALLBACK, new Object[]{serviceCredential.getId()}, request, service);
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug("No service credentials specified, and/or the proxy handler [{}] cannot handle credentials", this.proxyHandler);
}
// 触发验证成功的事件
onSuccessfulValidation(serviceTicketId, assertion);
LOGGER.debug("Successfully validated service ticket [{}] for service [{}]", serviceTicketId, service.getId());
// 返回成功视图
return generateSuccessView(assertion, proxyIou, service, request, ctxResult.getValue(), proxyGrantingTicketId);
}在 handleTicketValidation 方法中分别调用了以下方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| getServiceCredentialsFromRequest | 用于确定要使用哪些凭据来授予给 PGT(proxy granting ticket) 。默认情况是使用pgtUrl |
| handleProxyGrantingTicketDelivery | 处理代理授权票证传递 |
| validateServiceTicket | 验证服务票据 Assertion 信息 |
| validateAuthenticationContext | 验证认证上下文 |
| handleProxyIouDelivery | 获取 proxyIou |
| generateErrorView | 生成错误视图 |
| onSuccessfulValidation | 成功验证时触发事件。扩展此方法可作为钩子插入扩展行为。 |
| generateSuccessView | 生成成功视图 |
首先,我们看看,成功的时候,返回了什么?
private ModelAndView generateSuccessView(final Assertion assertion, final String proxyIou,
final WebApplicationService service, final HttpServletRequest request,
final Optional<MultifactorAuthenticationProvider> contextProvider,
final TicketGrantingTicket proxyGrantingTicket) {
// 根据获取 ModelAndView 对象
final ModelAndView modelAndView = getModelAndView(request, true, service);
// 填充返回的内容
modelAndView.addObject(CasViewConstants.MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_NAME_ASSERTION, assertion);
modelAndView.addObject(CasViewConstants.MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_NAME_SERVICE, service);
if (StringUtils.hasText(proxyIou)) {
modelAndView.addObject(CasViewConstants.MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_NAME_PROXY_GRANTING_TICKET_IOU, proxyIou);
}
if (proxyGrantingTicket != null) {
modelAndView.addObject(CasViewConstants.MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_NAME_PROXY_GRANTING_TICKET, proxyGrantingTicket.getId());
}
contextProvider.ifPresent(provider -> modelAndView.addObject(this.authnContextAttribute, provider.getId()));
final Map<String, ?> augmentedModelObjects = augmentSuccessViewModelObjects(assertion);
if (augmentedModelObjects != null) {
modelAndView.addAllObjects(augmentedModelObjects);
}
return modelAndView;
}到这里,我们再次看到了 getModelAndView 方法,说明此方法是一个通用的方法。我们就去看看 getModelAndView 方法的具体逻辑是什么样的?
private ModelAndView getModelAndView(final HttpServletRequest request, final boolean isSuccess, final WebApplicationService service) {
// 根据 service 对象参数判断响应的数据格式,默认 XML 格式
ValidationResponseType type = service != null ? service.getFormat() : ValidationResponseType.XML;
// 从请求中获取 format 参数,如果有指定该参数,则返回参数指定的数据格式
final String format = request.getParameter(CasProtocolConstants.PARAMETER_FORMAT);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(format)) {
try {
type = ValidationResponseType.valueOf(format.toUpperCase());
} catch (final Exception e) {
LOGGER.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
// 如果响应的数据格式是JSON类型,则返回 jsonView 视图
if (type == ValidationResponseType.JSON) {
return new ModelAndView(this.jsonView);
}
// 否则返回,successView 或 failureView 视图
return new ModelAndView(isSuccess ? this.successView : this.failureView);
}从上面的逻辑可看出,最终返回的内容是什么样的与 jsonView、successView、failureView 这三个视图对象有很大的关系。那这几个参数又是从哪里来的呢?
全局搜索源码,可以搜索到这几个参数是通过 AbstractServiceValidateController 的构造器注入进来的,那就可以去看看AbstractServiceValidateController的子类都有谁?
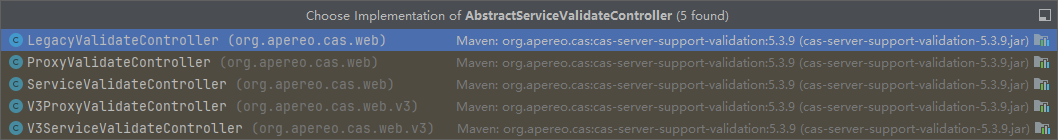
这里可看到与 验证有关的5个Controller,
- LegacyValidateController
- ProxyValidateController
- ServiceValidateController
- V3ProxyValidateController
- V3ServiceValidateController
继续全局搜索源码,可发现,上面的几个控制器都是在配置类 CasValidationConfiguration 中初始化出来的
V3ServiceValidateController
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "v3ServiceValidateController")
public V3ServiceValidateController v3ServiceValidateController() {
return new V3ServiceValidateController(
cas20WithoutProxyProtocolValidationSpecification,
authenticationSystemSupport.getIfAvailable(),
servicesManager,
centralAuthenticationService,
proxy20Handler.getIfAvailable(),
argumentExtractor.getIfAvailable(),
multifactorTriggerSelectionStrategy,
authenticationContextValidator,
cas3ServiceJsonView(),
cas3ServiceSuccessView(),
cas3ServiceFailureView,
casProperties.getAuthn().getMfa().getAuthenticationContextAttribute(),
serviceValidationAuthorizers,
casProperties.getSso().isRenewAuthnEnabled()
);
}V3ProxyValidateController
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "v3ProxyValidateController")
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "cas.sso", name = "proxyAuthnEnabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public V3ProxyValidateController v3ProxyValidateController() {
return new V3ProxyValidateController(
cas20ProtocolValidationSpecification,
authenticationSystemSupport.getIfAvailable(),
servicesManager,
centralAuthenticationService,
proxy20Handler.getIfAvailable(),
argumentExtractor.getIfAvailable(),
multifactorTriggerSelectionStrategy,
authenticationContextValidator,
cas3ServiceJsonView(),
cas3ServiceSuccessView(),
cas3ServiceFailureView,
casProperties.getAuthn().getMfa().getAuthenticationContextAttribute(),
serviceValidationAuthorizers,
casProperties.getSso().isRenewAuthnEnabled()
);
}通过源码,我们看到,这里有 cas3ServiceJsonView() 和 cas3ServiceSuccessView() 两个方法,cas3ServiceFailureView 全局对象。
我们进一步查看cas3ServiceSuccessView()这个方法,发现其是Cas30ResponseView 的实例化方法,这里我们需要关注 cas3SuccessView 参数
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "cas3ServiceSuccessView")
public View cas3ServiceSuccessView() {
final String authenticationContextAttribute = casProperties.getAuthn().getMfa().getAuthenticationContextAttribute();
final boolean isReleaseProtocolAttributes = casProperties.getAuthn().isReleaseProtocolAttributes();
return new Cas30ResponseView(true,
protocolAttributeEncoder,
servicesManager,
authenticationContextAttribute,
cas3SuccessView,
isReleaseProtocolAttributes,
authenticationAttributeReleasePolicy,
authenticationServiceSelectionPlan.getIfAvailable(),
cas3ProtocolAttributesRenderer());
}继续搜索源码,我们在 CasProtocolViewsConfiguration 对象代码中找到了 cas3SuccessView 这个方法
@Bean
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public CasProtocolView cas3SuccessView() {
return new CasProtocolView(casProperties.getView().getCas3().getSuccess(),
applicationContext, springTemplateEngine, thymeleafProperties);
}casProperties.getView().getCas3() 这段代码,可以找到配置对象 Cas30ViewProperties,通过查看这个配置对象,我们可以发现 CAS3 验证成功后的相对地址 protocol/3.0/casServiceValidationSuccess
public class Cas30ViewProperties implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2345062034300650858L;
/**
* The relative location of the CAS3 success validation bean.
*/
private String success = "protocol/3.0/casServiceValidationSuccess";
/**
* The relative location of the CAS3 success validation bean.
*/
private String failure = "protocol/3.0/casServiceValidationFailure";
...
}那如何找到这个 protocol/3.0/casServiceValidationSuccess 呢?前面讲到 Apereo CAS 当前主要是采用 Overlay 的方式进行扩展,那么我们一定会引入 War 包,比如我这里引入的是 Tomcat
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apereo.cas</groupId>
<artifactId>cas-server-webapp${app.server}</artifactId>
<version>${cas.version}</version>
<type>war</type>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>进入源码目录下找到此目录下的文件,我们可以看到 Cas 是使用 Thymeleaf 将 XML 渲染出来
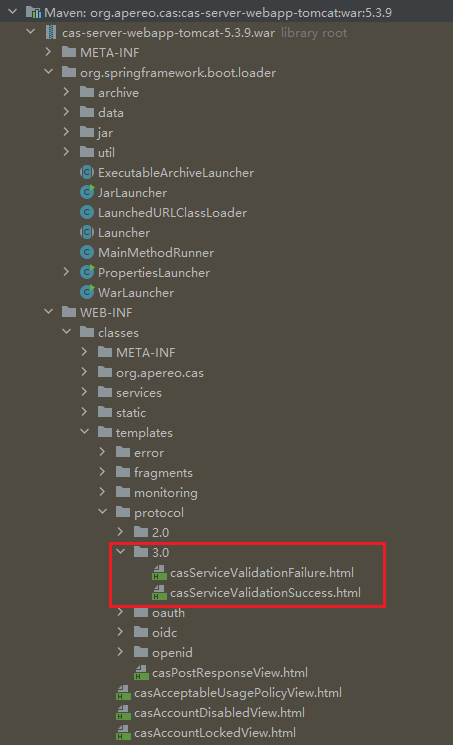
原始 casServiceValidationSuccess.html 文件
<cas:serviceResponse xmlns:cas='http://www.yale.edu/tp/cas'>
<cas:authenticationSuccess>
<cas:user th:text="${principal.id}"/>
<cas:proxyGrantingTicket th:if="${pgtIou}" th:text="${pgtIou}"/>
<cas:proxies th:if="${not #lists.isEmpty(chainedAuthentications)}">
<cas:proxy th:each="proxy : ${chainedAuthentications}" th:text="${proxy.principal.id}"/>
</cas:proxies>
<cas:attributes th:if="${not #lists.isEmpty(formattedAttributes)}">
<div th:each="attr : ${formattedAttributes}" th:remove="tag">
<div th:utext="${attr}" th:remove="tag"/>
</div>
</cas:attributes>
</cas:authenticationSuccess>
</cas:serviceResponse>这里可以看到 formattedAttributes 这个变量至关重要,它决定了返回的内容,搜索源码,找到了 CasProtocolConstants.VALIDATION_CAS_MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_NAME_FORMATTED_ATTRIBUTES 属性,通过这属性 我们又跟踪到了 Cas30ResponseView 对象的 putCasResponseAttributesIntoModel 方法:
protected void putCasResponseAttributesIntoModel(final Map<String, Object> model,
final Map<String, Object> attributes,
final RegisteredService registeredService) {
LOGGER.debug("Beginning to encode attributes for the response");
final Map<String, Object> encodedAttributes = this.protocolAttributeEncoder.encodeAttributes(attributes, registeredService);
LOGGER.debug("Encoded attributes for the response are [{}]", encodedAttributes);
super.putIntoModel(model, CasProtocolConstants.VALIDATION_CAS_MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_NAME_ATTRIBUTES, encodedAttributes);
final Collection<String> formattedAttributes = this.attributesRenderer.render(encodedAttributes);
super.putIntoModel(model, CasProtocolConstants.VALIDATION_CAS_MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_NAME_FORMATTED_ATTRIBUTES, formattedAttributes);
}可以看到,formattedAttributes 的源头是方法的 attributes 参数,顺着putCasResponseAttributesIntoModel 方法继续找,prepareMergedOutputModel,可以确定,最初源头是generateSuccessView 的 参数。
generateSuccessView(assertion, proxyIou, service, request, ctxResult.getValue(), proxyGrantingTicketId);回到 AbstractServiceValidateController 的 handleTicketValidation方法,可看到 Assertion 由 validateServiceTicket 方法产生;
final Assertion assertion = validateServiceTicket(service, serviceTicketId);进一步跟踪 validateServiceTicket 方法,可看到,此方法比较简单,主要是调用 CentralAuthenticationService 接口的 validateServiceTicket 方法
protected Assertion validateServiceTicket(final WebApplicationService service, final String serviceTicketId) {
return this.centralAuthenticationService.validateServiceTicket(serviceTicketId, service);
}根据查找 CentralAuthenticationService 接口的实现类,我们可以找到 DefaultCentralAuthenticationService 实现类
public Assertion validateServiceTicket(final String serviceTicketId, final Service service) throws AbstractTicketException {
// 验证票据的真实性
if (!isTicketAuthenticityVerified(serviceTicketId)) {
LOGGER.info("Service ticket [{}] is not a valid ticket issued by CAS.", serviceTicketId);
throw new InvalidTicketException(serviceTicketId);
}
// 根据 serviceTicketId 获取 Service ticket
final ServiceTicket serviceTicket = this.ticketRegistry.getTicket(serviceTicketId, ServiceTicket.class);
// 如果无法获取,则说明是无效的 Ticket
if (serviceTicket == null) {
LOGGER.warn("Service ticket [{}] does not exist.", serviceTicketId);
throw new InvalidTicketException(serviceTicketId);
}
try {
/*
* Synchronization on ticket object in case of cache based registry doesn't serialize
* access to critical section. The reason is that cache pulls serialized data and
* builds new object, most likely for each pull. Is this synchronization needed here?
*/
synchronized (serviceTicket) {
// 检查 Service ticket 是否过期
if (serviceTicket.isExpired()) {
LOGGER.info("ServiceTicket [{}] has expired.", serviceTicketId);
throw new InvalidTicketException(serviceTicketId);
}
// 检查 Service ticket 是否
if (!serviceTicket.isValidFor(service)) {
LOGGER.error("Service ticket [{}] with service [{}] does not match supplied service [{}]",
serviceTicketId, serviceTicket.getService().getId(), service);
throw new UnrecognizableServiceForServiceTicketValidationException(serviceTicket.getService());
}
}
// 从认证请求中解析 Service
final Service selectedService = resolveServiceFromAuthenticationRequest(serviceTicket.getService());
LOGGER.debug("Resolved service [{}] from the authentication request", selectedService);
// 检查服务是否可以访问
final RegisteredService registeredService = this.servicesManager.findServiceBy(selectedService);
LOGGER.debug("Located registered service definition [{}] from [{}] to handle validation request", registeredService, selectedService);
RegisteredServiceAccessStrategyUtils.ensureServiceAccessIsAllowed(selectedService, registeredService);
// 从 Service ticket 获取 TGT
final TicketGrantingTicket root = serviceTicket.getTicketGrantingTicket().getRoot();
// 从TGT授权信息获取 Authentication 对象
final Authentication authentication = getAuthenticationSatisfiedByPolicy(root.getAuthentication(),
new ServiceContext(selectedService, registeredService));
// 从 Authentication 获取旧的 Principal 对象
final Principal principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
// 从服务配置中获取最终返回的属性保留策略,如果这个对象不为空则决定了下面最终返回的属性
final RegisteredServiceAttributeReleasePolicy attributePolicy = registeredService.getAttributeReleasePolicy();
LOGGER.debug("Attribute policy [{}] is associated with service [{}]", attributePolicy, registeredService);
// 创建新的 attributesToRelease
final Map<String, Object> attributesToRelease = attributePolicy != null
? attributePolicy.getAttributes(principal, selectedService, registeredService) : new HashMap<>();
LOGGER.debug("Calculated attributes for release per the release policy are [{}]", attributesToRelease.keySet());
// 获取 principalId
final String principalId = registeredService.getUsernameAttributeProvider().resolveUsername(principal, selectedService, registeredService);
// 使用 PrincipalFactory 创建新的 Principal。这个地方很重要,是扩展的核心
final Principal modifiedPrincipal = this.principalFactory.createPrincipal(principalId, attributesToRelease);
final AuthenticationBuilder builder = DefaultAuthenticationBuilder.newInstance(authentication);
builder.setPrincipal(modifiedPrincipal);
LOGGER.debug("Principal determined for release to [{}] is [{}]", registeredService.getServiceId(), principalId);
// 构建最终的认证信息
final Authentication finalAuthentication = builder.build();
// 创建审计上下文
final AuditableContext audit = AuditableContext.builder().service(selectedService)
.authentication(finalAuthentication)
.registeredService(registeredService)
.retrievePrincipalAttributesFromReleasePolicy(Boolean.FALSE)
.build();
// 执行审计逻辑
final AuditableExecutionResult accessResult = this.registeredServiceAccessStrategyEnforcer.execute(audit);
accessResult.throwExceptionIfNeeded();
// ThreadLocal 绑定最终的认证信息
AuthenticationCredentialsThreadLocalBinder.bindCurrent(finalAuthentication);
// 创建 Assertion 对象
final Assertion assertion = new DefaultAssertionBuilder(finalAuthentication)
.with(selectedService)
.with(serviceTicket.getTicketGrantingTicket().getChainedAuthentications())
.with(serviceTicket.isFromNewLogin())
.build();
// 推送 CasServiceTicketValidatedEvent 事件
doPublishEvent(new CasServiceTicketValidatedEvent(this, serviceTicket, assertion));
return assertion;
} finally {
if (serviceTicket.isExpired()) {
deleteTicket(serviceTicketId);
} else {
this.ticketRegistry.updateTicket(serviceTicket);
}
}
}从上面的代码逻辑分析可得出结论,影响最终输出的认证结果信息的有2个逻辑:
第一段:原始数据的处理,这段逻辑过程为:查询票据 -> 从票据获取认证信息 -> 从认证信息获取 Principal -> 根据服务的属性保留策略,返回最后的属性
// 从 Service ticket 获取 TGT
final TicketGrantingTicket root = serviceTicket.getTicketGrantingTicket().getRoot();
// 从TGT授权信息获取 Authentication 对象
final Authentication authentication = getAuthenticationSatisfiedByPolicy(root.getAuthentication(),
new ServiceContext(selectedService, registeredService));
// 从 Authentication 获取旧的 Principal 对象
final Principal principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
// 从服务配置中获取最终返回的属性保留策略,如果这个对象不为空则决定了下面最终返回的属性
final RegisteredServiceAttributeReleasePolicy attributePolicy = registeredService.getAttributeReleasePolicy();
LOGGER.debug("Attribute policy [{}] is associated with service [{}]", attributePolicy, registeredService);
// 创建新的 attributesToRelease
final Map<String, Object> attributesToRelease = attributePolicy != null
? attributePolicy.getAttributes(principal, selectedService, registeredService) : new HashMap<>();
LOGGER.debug("Calculated attributes for release per the release policy are [{}]", attributesToRelease.keySet());第二段:认证授权信息的二次处理,这段逻辑过程为:从旧的Principal获取 principalId -> 基于旧的 Principal 创建一个新的Principal -> 构建认证结果对象
final String principalId = registeredService.getUsernameAttributeProvider().resolveUsername(principal, selectedService, registeredService);
final Principal modifiedPrincipal = this.principalFactory.createPrincipal(principalId, attributesToRelease);
final AuthenticationBuilder builder = DefaultAuthenticationBuilder.newInstance(authentication);
builder.setPrincipal(modifiedPrincipal);
LOGGER.debug("Principal determined for release to [{}] is [{}]", registeredService.getServiceId(), principalId);
final Authentication finalAuthentication = builder.build();两端代码,给了我们两种不一样的改造思路:
改造方案1
- 修改
DefaultCentralAuthenticationService的validateServiceTicket方法中的Map<String, Object> attributesToRelease处代码,新增扩展的属性 - 修改
casServiceValidationSuccess.html文件,新增新的返回属性
改造方案2
- 自定义新的
CentralAuthenticationService实现类,注入Spring取代默认的DefaultCentralAuthenticationService - 自定义新的
PrincipalFactory实现类,注入Spring取代默认的DefaultPrincipalFactory
综合会考虑我认为,方案一,改造简单,但是对代码逻辑污染较重,且会照成返回内容不标准,三方对接时,注意事项较多。方案二改造需要覆盖对象多,但是代码解耦,继续采用原有的数据结构,对接是影响较小。
4、实施改造方案2【推荐】
自定义 PrincipalFactory 实现类,实现从Redis缓存中获取自定义属性
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class MyPrincipalFactory implements PrincipalFactory {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3999695695604948495L;
private RedisTemplate userRedisTemplate;
public MyPrincipalFactory(final RedisTemplate userRedisTemplate) {
this.userRedisTemplate = userRedisTemplate;
}
@Override
public Principal createPrincipal(final String id, final Map<String, Object> attributes) {
// 1、门户登录成功后,会记录登录信息到缓存中(此处代码很重要,是实现全局统一认证信息的一部分)
String rdsKey = BizRedisKey.USER_LOGIN_INFO.getKey(id);
// 1.1、从缓存获取登录信息
Map<String, Object> loginInfoMap = userRedisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(rdsKey);
// 1.2、设置缓存中登录信息到 Principal
attributes.put("loginInfo", loginInfoMap);
return new SimplePrincipal(id, attributes);
}
}
注入自定义 PrincipalFactory 到 Spring 上下文,覆盖默认实现:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apereo.cas.authentication.principal.MyPrincipalFactory;
import org.apereo.cas.authentication.principal.PrincipalFactory;
import org.apereo.cas.configuration.CasConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectProvider;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration("casCoreExtConfiguration")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CasConfigurationProperties.class)
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
@Slf4j
public class CasCoreExtConfiguration {
@Bean(name = "principalFactory")
public PrincipalFactory principalFactory(ObjectProvider<RedisTemplate> userRedisTemplate){
return new MyPrincipalFactory(userRedisTemplate.getIfAvailable());
}
}参考资料:
最后编辑:Jeebiz 更新时间:2024-05-06 16:13
